Warning signs and risk factors of myeloid leukemia
Myeloid leukemia, a type of cancer, is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects the blood and bone marrow. It could develop in individuals of all ages, making it important to understand its early signs and risk factors. So, one should explore the key aspects of myeloid leukemia, including the early signs and the factors that increase the risk of developing this disease. Early awareness and detection significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
Understanding myeloid leukemia
Myeloid leukemia refers to a type of cancer that develops in the bone marrow. To understand this disease better, knowing how the blood-forming process normally works is essential. The bone marrow produces various types of blood cells, including white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. These cells play crucial roles in carrying oxygen, fighting infections, and preventing excessive bleeding.
In myeloid leukemia, a specific type of white blood cell called a myeloid cell becomes cancerous. This leads to the uncontrolled production of abnormal myeloid cells, crowding out healthy blood cells in the bone marrow and bloodstream. As a result, the body’s ability to perform essential functions, such as fighting infections and transporting oxygen, is compromised.
The signs
Detecting myeloid leukemia in its early stages might be challenging because its symptoms often mimic those of various other health conditions. However, there are certain signs and symptoms that individuals should be aware of, which may require an expert’s opinion.
- Fatigue
Fatigue is a common and debilitating symptom in individuals with myeloid leukemia. This type of cancer disrupts the average production of red blood cells, leading to anemia. As a result, the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity is impaired, causing persistent tiredness and weakness. This fatigue could be overwhelming and interfere with daily activities, significantly impacting the quality of life for those battling myeloid leukemia. - Frequent infections
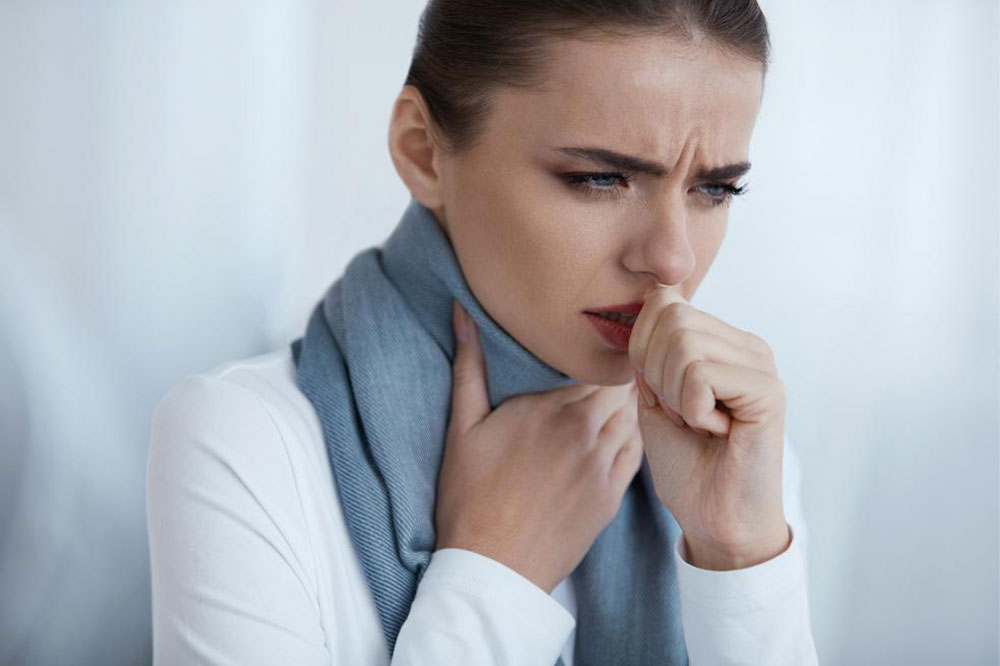
Frequent infections are a common concern for individuals with myeloid leukemia. The disease compromises the immune system, making it less effective at fighting infections. This increased susceptibility to infections might lead to recurrent illnesses, such as respiratory or urinary tract infections, and may sometimes be severe or difficult to manage. Anyone who notices frequent infections should speak to an expert about the same. - Unexplained bruising or bleeding
In myeloid leukemia, unexplained bruising or bleeding might occur due to a decrease in platelet count, which impairs the body’s ability to form blood clots. As a result, even minor injuries or bumps might lead to excessive bleeding or the appearance of unexplained bruises. Individuals should seek healthcare-oriented attention for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis to rule out underlying health concerns. - Pain in the bones
Bone pain may arise due to the overcrowding of cancerous cells in the bone marrow, disrupting the normal bone tissue and causing discomfort. Bone pain is most commonly felt in the hips and legs. It might range from a dull ache to sharp, intense pain and often worsens with physical activity. Proper pain management and help from healthcare experts are essential to alleviate this aspect of the disease’s burden. - Swollen lymph nodes
Swollen lymph nodes are a common symptom of myeloid leukemia. In this condition, cancerous myeloid cells often infiltrate the lymph nodes, causing them to enlarge. This could lead to visible swelling in areas like the neck, armpits, or groin. Swollen lymph nodes may be tender or painless and serve as a significant indicator. - Fever and night sweats
In myeloid leukemia, fever and night sweats often manifest as distressing symptoms. These sweats are typically drenching and may disrupt a patient’s sleep patterns, contributing to overall discomfort. Fever is usually unexplained and persistent, signaling the body’s struggle against the cancerous cells and the impaired immune system’s response.
It’s important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to myeloid leukemia and might occur in people affected by other health conditions. However, if these symptoms persist or worsen, it is imperative to seek help from a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis.
People at risk of myeloid leukemia
Myeloid leukemia might affect individuals of all ages, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this cancer. Knowing these risk factors can help individuals and healthcare providers identify those at higher risk and take appropriate preventive measures or early detection strategies:
- Age
Myeloid leukemia is commonly seen in older adults, with the risk increasing with age. However, it might occur in individuals of all age groups, including children. - Gender
Some studies suggest that men may have a slightly higher risk of developing myeloid leukemia than women. - Genetic factors
In some cases, myeloid leukemia might be linked to genetic factors. Individuals with certain genetic syndromes, such as Down syndrome or Fanconi anemia, may have an increased risk. - Exposure to radiation and harmful properties
High levels of exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from previous cancer treatments or nuclear accidents, may increase the risk of myeloid leukemia. Similarly, exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene, has been associated with a higher risk of the disease. - Prior cancer treatments
Individuals who have undergone specific cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, may be at an increased risk of developing secondary myeloid leukemia. - Family history
While rare, myeloid leukemia may run in families, indicating a potential genetic predisposition. Individuals with a family history of the disease may have a slightly higher risk. - Blood disorders
Some blood disorders, such as myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), could increase the risk of developing myeloid leukemia. - Immune system suppression
Conditions or treatments that suppress the immune system, such as organ transplantation or certain prescriptions, might raise the risk of myeloid leukemia.
It’s important to emphasize that having one or more risk factors does not indicate the development of myeloid leukemia. Conversely, individuals without known risk factors may still develop the disease. Therefore, regular check-ups and health screenings are essential for early detection and improved outcomes.


