Eczema – Types, symptoms, causes, and management
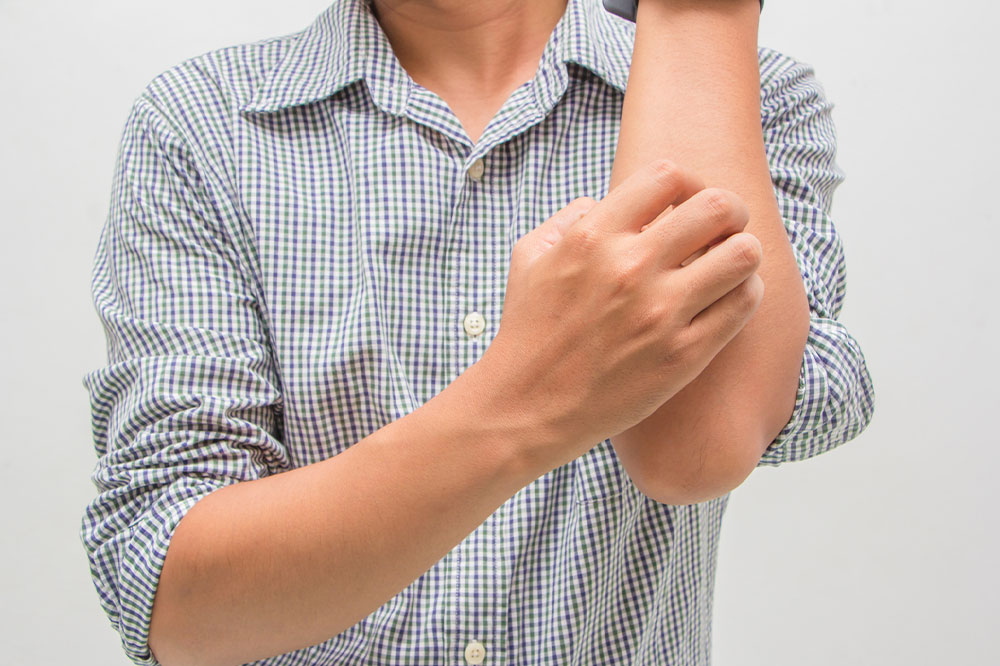
Eczema is a prevalent skin disease that causes the skin to become dry, flaky, itchy, and bumpy. It mainly weakens the skin barrier, which is responsible for keeping the skin moisturized and protecting the body from external elements. When this barrier does not function efficiently, it can lead to inflammation and trigger various signs and symptoms. Read on to learn about eczema, its types, symptoms, causes, treatments, and helpful natural remedies.
Types
There are different types of this skin disease, each with unique triggers that can affect the functioning of the skin barrier. Some common examples are:
Atopic dermatitis
This disorder is characterized by skin discoloration and the formation of itchy patches on the skin. Many people develop atopic dermatitis in childhood and face flare-ups through adulthood. While it has no cure, one can manage the symptoms with treatment.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is an allergic reaction caused due an allergen or irritant. It is not contagious and can be prevented.
Dyshidrotic eczema
It is a condition that leads to blisters on the skin. Individuals may also experience itching and discomfort. Several things can trigger dyshidrotic eczema, including allergies and stress, but the most common trigger is sweaty palms and feet.
Neurodermatitis
Like atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis can lead to itchy patches and skin discoloration. There could also be severe itching and dryness based on the condition’s severity. The itch can occur on any body region but is most commonly seen on the arms, shoulders, elbows, legs, wrists, and scalp. Further, it may cause the skin to have a leathery texture.
Nummular eczema
Nummular eczema is a severe condition that can lead to raised and round spots on the skin. These spots and lesions are typically shaped like a coin and can sometimes ooze clear fluids. It is not curable and can be managed with proper treatment and prevention methods.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis appears as red, itchy, and flaky skin on various body parts, including the scalp. Although a common skin disease, it is not contagious.
Symptoms
Eczema can be identified by various symptoms, each with unique characteristics and features. But, experts have found a few signs commonly seen across various types of this skin disease. These include dry skin, itchiness on various parts of the body, rashes, flaky or crusty skin, clear fluids oozing from the skin, swelling, leathery patches of skin, and raised, red, bumps on the skin. These symptoms can appear anywhere, but the most commonly affected areas are the hands, feet, neck, elbows, ankles, face, lips, and in and around the ears. The least affected areas are usually the nipples, breasts, and penis.
It is important to note that eczema can look different on different individuals. For example, eczema rashes may appear purple, brown, or even grayish on darker skin tones. On lighter skin tons, the same rash could look purple or red. The severity of the condition may also affect how the signs manifest. Those with severe eczema may notice more symptoms, discomfort, or pain than those with milder episodes.
Causes
There are no exact known causes for eczema. But, experts say that a few risk factors could increase a person’s chances of developing this skin disease. Some of these common triggers include:
Immune system reactions
In many cases, eczema results from the immune system overreacting to harmless irritants or allergens. It happens when the body’s immune system considers these tiny irritants foreign invaders, such as bacteria or viruses. It then triggers an inflammatory response to tackle the issue. But, of course, in reality, there are no bacteria or viruses, and this unnecessary inflammatory reaction from the immune system leads to eczema.
Genetic predisposition and family history
Genetics also plays a vital role in the development of such skin diseases. Studies have found that individuals are more likely to get eczema when it runs in the family. A genetic mutation could affect how the skin barrier functions. Such individuals may also be at high risk for hay fever, asthma, and allergies.
Environmental factors
Many external factors could lead to the development of eczema. The list includes skincare products, harsh soaps, pollutants, irritants like wool, and allergens like pollen and pet hair. Humidity could also cause the skin to become dry and itchy, triggering eczema.
Poor emotional health
An individual’s poor emotional and mental health could also trigger the ailment. High levels of stress, anxiety, and depression are known to lead to more flare-ups.
Treatments
There is no cure for eczema, but the treatments available can help prevent flare-ups and reduce the severity of the condition. The aim is to enable individuals to live discomfort-free lives and ensure they can function without being bothered by this skin disease. However, the treatments can take time to work and must be used correctly for the best results in the long term.
Several treatment options are available to treat eczema. Most of them help reduce inflammation, itching, and swelling. Light therapy, a popular alternative, improves the skin’s appearance and reduces dark patches. Doctors may also prescribe topical applications to help deal with itchiness and inflammation. Further, skin-sensitive moisturizers and soaps may help people with dry skin.
Natural remedies
Besides treatments recommended by the doctor, individuals may try home remedies to relieve the symptoms. Aloe vera gel is known to have many anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe eczema and help heal wounds. Applying apple cider vinegar to the affected areas can help balance the skin’s acidity levels, reduce dryness and itching, and fight bacteria. Bleach baths, colloidal oatmeal, coconut oil, and tea tree oil are other suitable natural remedies for managing this skin disease. However, it is essential to check with a healthcare professional before trying these home remedies to prevent the risk of complications.


