Eczema in babies, kids, and teens – Signs and management
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common and often chronic skin condition that affects individuals of all ages. However, it can manifest differently in babies, kids, and teenagers. Knowing the signs, symptoms, and effective management strategies for eczema at each developmental stage is crucial for providing relief and improving the quality of life for young individuals and their families. So, here is a brief guide to understanding eczema in babies, kids, and teenagers.
Eczema in babies (0-2 years)
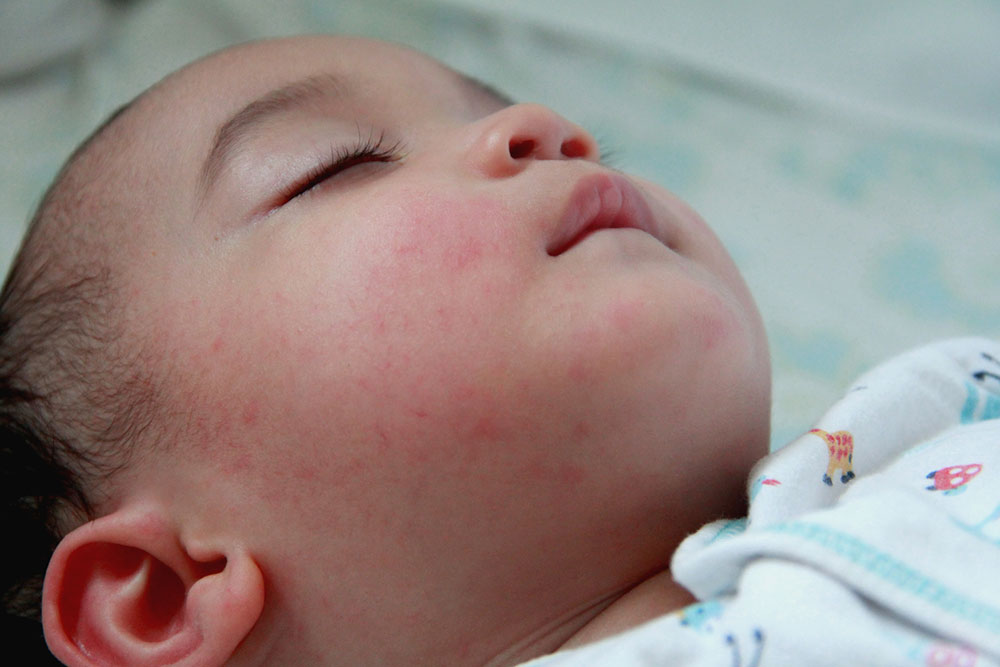
Eczema in babies, often referred to as infantile eczema, presents unique challenges for parents. While it commonly appears on the cheeks and scalp, it can affect any part of the body.
- Early signs and symptoms
Infantile eczema typically starts with red, itchy, and inflamed patches on the cheeks and scalp. These patches may spread to other areas, such as the arms, legs, and torso. Scratching can worsen the condition, leading to broken skin and potential infections. This can be especially distressing for young infants who are unable to express their discomfort verbally. - Causes and triggers
The exact cause of eczema in babies is still unknown, but genetics and environmental factors play a significant role in its development. Common triggers include exposure to allergens, irritants like harsh soaps, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Management and care
Managing eczema in babies involves meticulous care. Parents should prioritize the following:
- Keep the baby’s skin moisturized with fragrance-free, hypoallergenic creams or ointments.
- Dress the baby in soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid tight clothing to reduce friction and irritation.
- Maintain a consistent bathing routine with lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free baby soap. Avoid bathing them with hot water, as it might aggravate the symptoms.
- Gently pat the baby’s skin dry after bathing to avoid further irritation.
- Consult a pediatrician or dermatologist for personalized treatment options. They can also guide parents in identifying and minimizing potential triggers, helping to provide much-needed relief for both the baby and their caregivers.
Eczema in kids (3-12 years)
Eczema, as kids transition from toddlers to preadolescents, may persist or evolve. And identifying triggers for eczema flare-ups in children becomes essential for effective management.
- Signs and symptoms
The red, itchy, and scaly patches commonly occur on the elbows and knees, but they can develop on other body parts, too. This can also cause discomfort and sleep disturbances. For kids, eczema can be more than a physical nuisance; it can affect their self-esteem, particularly if the condition is visible and prone to flare-ups regularly. - Causes and triggers
Identifying triggers for eczema flare-ups in children is essential for effective management. Common triggers include allergens like pollen or pet dander, stress, and certain foods (such as dairy or nuts). By identifying and minimizing these triggers, parents can help their children experience fewer and less severe flare-ups.
Management and care
- Continue regular moisturization with non-fragranced creams or ointments.
- Trim the child’s nails to prevent scratching-related injuries and infections.
- Consider allergy testing to identify potential food triggers.
- Avoid bathing them with hot water, and instead, switch to lukewarm water when required.
- Encourage stress-reduction techniques appropriate for the child’s age, such as relaxation exercises or play therapy.
- Work with a pediatrician or dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan. These professionals can also offer guidance on managing eczema in school settings, including how to communicate with teachers and school nurses to ensure the child receives the necessary care and accommodations.
Eczema in teens (13-18 years)
Teenagers face unique challenges when managing eczema. As they undergo hormonal changes, eczema symptoms can become more unpredictable. Here’s what they and their parents need to consider:
- Signs and symptoms
Eczema may persist into adolescence, impacting areas like the hands, feet, and face. It can also trigger self-esteem and body image issues, so emotional support by parents and guardians is crucial. - Causes and triggers
Teenagers should be aware of potential triggers, such as hormonal changes, stress related to academics and social pressures, and exposure to harsh skincare products. Additionally, lifestyle factors like food choices and exercise can impact eczema severity.
Management and care
- Encourage open communication with the teenager about their eczema concerns.
- Help them establish a consistent skincare routine, emphasizing the use of gentle, fragrance-free products.
- Encourage them to follow and maintain a balanced meal rich in anti-inflammatory and omega-3 fatty acids like fruits and vegetables.
- Advise them to avoid bathing with hot water or taking hot showers. Ask them to switch to lukewarm water for bathing instead.
- Explore stress management techniques like mindfulness, yoga, or counseling.
- Consult a dermatologist for advanced treatment options. Additionally, dermatologists can provide guidance on managing the condition during activities like sports and advise on skincare routines that suit a teenager’s lifestyle.
Diagnosing eczema across age groups
In all age groups, the diagnosis of eczema typically begins with a thorough clinical examination conducted by a healthcare provider, which can be a pediatrician, dermatologist, or allergist, depending on the circumstances. Doctors evaluate the patient’s health history, family history of skin conditions or allergies, and the specific symptoms observed. Eczema is often diagnosed based on the presence of hallmark signs like redness, inflammation, intense itching, and the characteristic appearance of dry, scaly patches. In some cases, doctors may perform patch testing or allergy tests to identify potential triggers or rule out other skin conditions that may mimic eczema. A precise diagnosis is crucial to develop an effective management plan tailored to the patient’s age and needs, ensuring that the best possible care is provided throughout childhood and adolescence.
Eczema can impact individuals throughout their formative years, presenting unique challenges at each stage of development. However, with early recognition, effective management, and emotional support, children and teenagers can lead comfortable and fulfilling lives despite eczema. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in guiding and empowering their loved ones to manage eczema effectively. By addressing this condition holistically and seeking professional guidance, families can help their children navigate eczema with confidence and resilience, ultimately leading to improved skin health and overall well-being.


