6 most common IUD myths debunked
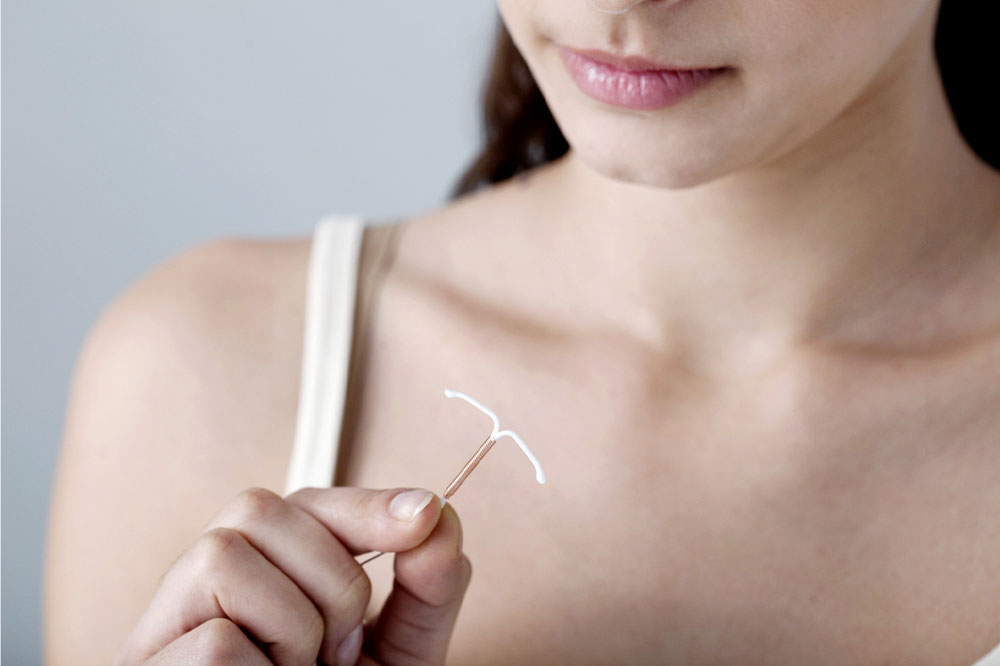
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are among the most popular and safe contraceptive options for long-term protection against pregnancy. But despite the good results and positive user feedback, some women hesitate to use them. One reason is that they believe in the myths about IUDs and do not understand how they work. Considering this, we decided to clear the misconceptions once and for all. First, let us understand what IUDs are and how they are used.
What are IUDs?
IUDs are long-acting T-shaped contraceptive devices placed inside the uterus. They can be categorized into two types: non-hormonal and hormonal. Non-hormonal IUDs are generally made of copper, which intercepts and kills sperm, preventing them from fertilizing the egg. Hormonal options release progestin, a hormone that thickens a woman’s cervical mucus, preventing the male reproductive cells from reaching the egg.
IUDs are easy to place inside the uterus and can be removed to induce conception. Women who have concerns and questions about the procedure or find it hard to choose an IUD brand can speak to a healthcare professional. Experts always recommend products approved by the FDA.
Common IUD myths debunked
As a contraception method surges in popularity, so do the myths associated with it. The hesitation among women about IUDs is sometimes due to the comparison with older versions of the contractive device, which were often associated with pelvic inflammatory diseases. However, it helps to note that older IUDs have been discontinued and replaced by modern alternatives.
Here, we have put together a few circulating IUD myths and debunked them by revealing the facts:
- Myth 1: IUDs can result in infertility
“Can IUDs cause infertility?” is a frequently asked question on the internet. While some websites say the method can result in infertility, it is a misconception with no real facts. Healthcare professionals suggest IUDs are a long-term approach to preventing pregnancy. They can be inserted inside a woman’s uterus to prevent sperm from meeting the egg. However, the effect lasts only as long as the device is in place. An expert can remove the IUD if the user wants to have children.
- Myth 2: IUDs are only for women with children or older women
This myth has been around for various reasons but must be ignored. IUDs are suitable for women of all ages, from their teenage years till perimenopause. Some out-of-date practitioners discourage women from using IUDs if they are young or yet to have a baby. But the latest research suggests that IUDs are an excellent contraception mode for every woman.
- Myth 3: IUDs can cause infections in the uterus
This myth is generally associated with the IUDs of the early 1970s. Many women who used them would develop infections in the uterus. However, health science has come a long way since then, and modern IUDs no longer pose a risk of infection. They are proven to have the best results and can be used without worrying. Most brands that manufacture IUDs test their products for potential side effects and safety and get approvals from the FDA before launching them. The World Health Organization has also stated that modern IUDs are about 99% effective, and users are not susceptible to pelvic infections.
- Myth 4: IUD insertion is painful
Women planning to get an IUD often hear that the insertion process is extremely painful. Sadly, such misconceptions deter them from opting for the method. During the IUD insertion, women may feel slight discomfort only, quite similar to that experienced during a Pap smear procedure, or cramps from the menstrual cycle. Even though the pain threshold range varies among users, most women confidently handle the entire process. Before proceeding with the procedure, one also has the option to use treatments that numb the area and reduce pain sensation. Further, women can schedule IUD insertion during the first or second day of their menstrual cycle, when the cervix is naturally dilated, reducing the discomfort.
- Myth 5: IUDs can fall out or get displaced
Women tend to avoid IUDs, fearing they will fall out during physical activity and need regular adjustments. Some even believe that the device will move from their uterus to the stomach and, in the worst cases, even the chest! While an IUD device can fall out or move around the uterus, the chances are next to zero. In most cases, they are positioned to stay in place without causing problems. If required, one can even check the device for proper positioning at home without expert assistance.
- Myth 6: One’s partner might feel the IUD
When inserted correctly, it is impossible for one’s partner to feel the IUD during intercourse. This is because they are positioned in the uterus, not the cervix. The only part that may be felt is the device’s string hanging out. Doctors usually trim the strings to make it as inconspicuous as possible. But if a user feels the strings, they can consult a doctor and have it trimmed in no time. If one’s partner can feel the IUD device, it indicates it is not positioned correctly and will be ineffective in protecting against pregnancy. In such circumstances, women may schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional.
Most IUD myths and misconceptions are linked to their safety and efficiency as a contraceptive method. However, they are among the best, most convenient, and safest modes of birth control for many women as long as they need it. They do not affect fertility in the future and are associated with milder side effects, which resolve after a few days. Women can consult a healthcare professional to choose the type of IUD that fits their requirements and clarify their doubts before signing up for the procedure.


